Robotic arms are used across nearly every industry, but their largest sector by far is manufacturing.
By increasing productivity, efficiency, and overall profitability, they can complete work faster and with more precision than is humanly possible.
Flexiv's series of adaptive robotic arms go beyond traditional position-based control by combining industrial-grade force sensing with artificial intelligence. This endows our robots with a sense of touch and an ability to think, enabling them to not only follow fixed trajectories but also interact in real-time with their environments.
From automotive and electronics to pharmaceuticals and food processing, industries around the world are embracing adaptive automation to increase competitiveness, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
Core Features of a Robotic Arm
A robotic arm, much like a human arm, consists of multiple joints, which in robotics are referred to as degrees of freedom.
The more degrees of freedom an arm has, the more flexible it becomes and the better it can maneuver into various positions. As degrees of freedom increase, the time needed to complete complex tasks is reduced due to the more efficient movement that is possible.
Traditional collaborative robots typically have five or six degrees of freedom. Flexiv's robotic arms, however, like that of a human, have seven.
At the end of your arm is a hand, and at the end of a robotic arm is what's called the “end-of-arm tool.” This is where tools such as grippers, sanders, pneumatic vacuums, or even robotic hand facsimiles are attached.
Featuring a universal mounting flange, virtually any end-of-arm tool can be mounted to a Rizon series adaptive arm. This might be one of our own Grav series robot grippers or even a standard DIY tool fitted using a mounting bracket.
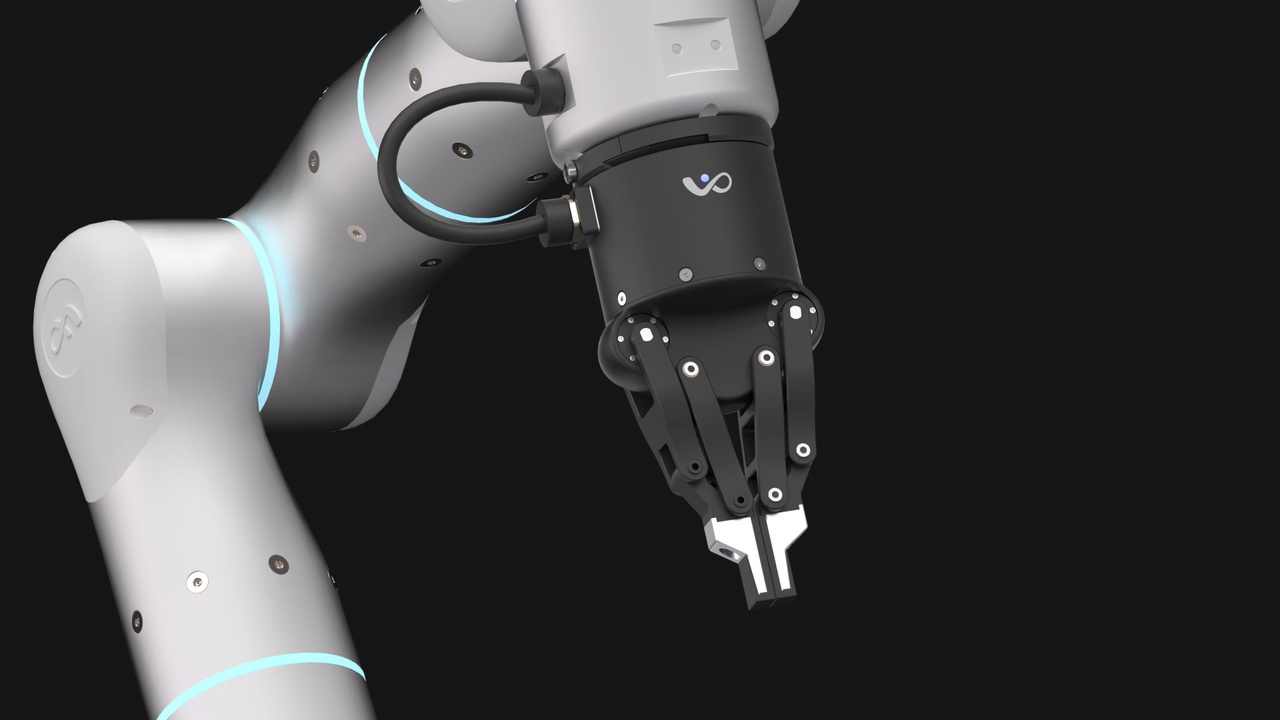
What Makes a Robotic Arm Move?
Instead of muscles, robotic arms typically use electric motors called actuators or servo motors. These motors are equipped with encoder devices so the robot always knows the position of each joint, enabling coordinated movement.
This is similar to the human sense of proprioception, which provides us with an ability to sense the position and movement of our body without looking.
While all robots must have some form of encoder, Flexiv's adaptive robots feature absolute encoders on each axis. This means that even if the robot is physically moved while powered off, it will instantly know its position upon restarting.
Alongside encoders, robots can also use computer vision systems, or cameras, giving them a sense of sight, alongside sensors to measure force.
Flexiv's adaptive robots feature force-torque sensors on each joint, enabling whole-body force control at an industry-leading sensitivity of 0.03 newtons.
Our proprietary control algorithms then allow our adaptive robots to respond intelligently to their environment, adjusting in real time to variations in the workpiece or task.
Common Applications for Robotic Arms
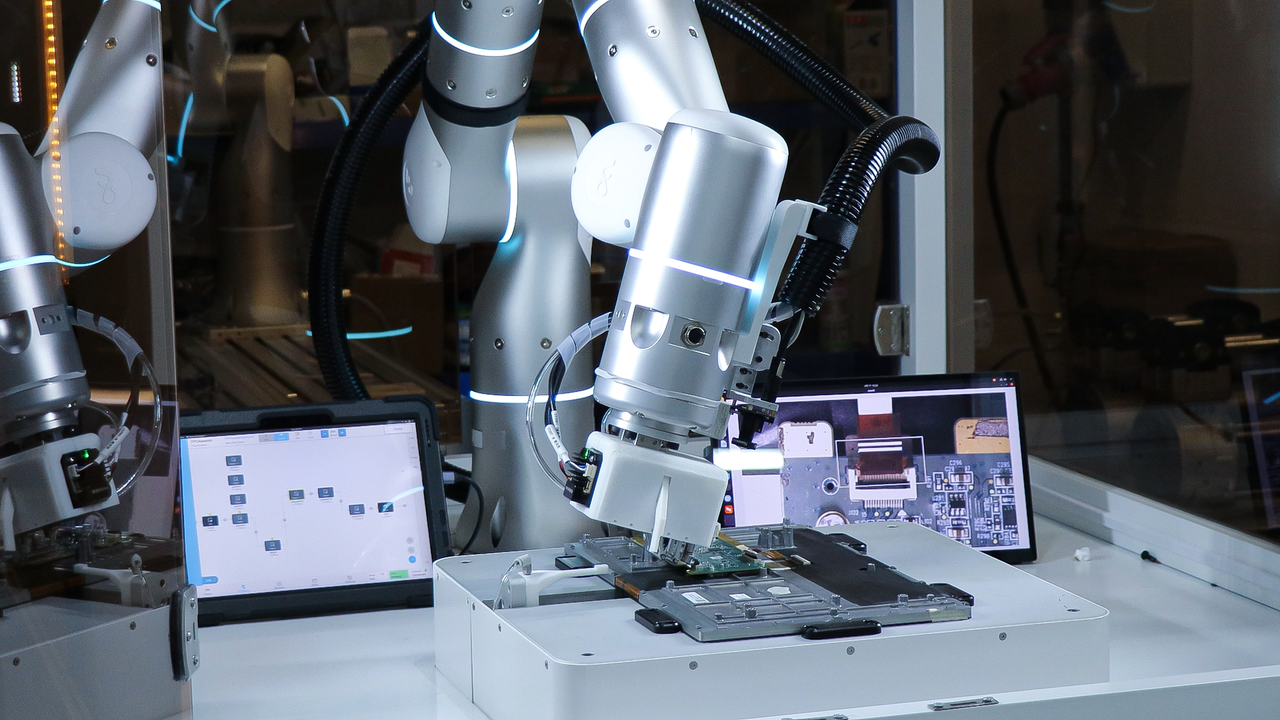
Robotic arms excel in a wide variety of manufacturing applications. In assembly operations, they can rapidly and precisely fit components together. This commonly takes the form of inserting electronic parts into circuit boards or screw fastening operations.
While all robots can perform this thanks to position-based control, Flexiv's adaptive robots use AI and advanced sensors to detect misalignments and automatically compensate for them.
This may sound trivial but imagine a production line where a motherboard must be screwed into a phone housing. A variation of just 0.5 mm can be the difference between a functional device and a ruined one.

Robot arms can also be used for material-handling where they efficiently transport items throughout the manufacturing process. This commonly takes the form of loading raw materials and picking and packing finished goods.
By simply changing the end-of-arm tool, almost any robot can be configured for material handling.
For added versatility, robotic arms can also be mounted on AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) or AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles), allowing them to move objects between locations autonomously.
Advantages of Using Robotic Arms in Manufacturing
There are numerous benefits to using robotic arms in a manufacturing setting.
First and foremost is precision and repeatability. Robotic arms allow operators to replicate movements and actions with an accuracy far beyond human capabilities.
This precision is paired with reduced operational costs, the elimination of human error, and the ability to operate continuously.
Adaptive robots offer even greater benefits through their ability to function unsupervised by adapting to variations in the environment, be these variations misaligned parts or unexpected interference.
Where a conventional trajectory-based robot would stop production upon encountering an obstacle, an adaptive robot from Flexiv can actively adjust, making true “lights-out” manufacturing possible.
Programming and Line Changeovers
All robots can be reprogrammed, allowing them to be repurposed for different tasks. With only minor changes to their code and end-of-arm tooling, a robot might handle confectionery one day and perform screw-fastening the next.
This flexibility makes robotic arms a multi-role investment that extends well beyond their initial application.
Programming complexity for these applications though varies depending on the robot. While older industrial robots required complex coding, Flexiv's adaptive robots can be easily programmed by guiding the arm manually and using drag-and-drop function blocks within the Elements programming environment.
For more advanced application creation, Flexiv's robots also support traditional coding languages such as C++ and Python through the Robot Development Kit (RDK).
Future Robotic Trends in Manufacturing
As technology improves, so do robots and the scope of their applications.
Today's most advanced robots utilize embodied intelligence to optimize movements and improve performance through experience.
This allows them not only to learn how to complete tasks more efficiently but also to transfer those skills to similar tasks.
Flexiv is actively building upon this technology, in order to create a general robotic intelligence that is capable of executing tasks with minimal or even no programming.
Simultaneously, advances in sensor technology are enhancing robotic abilities by improving vision systems and tactile feedback mechanisms.
Through being able to better sense and understand its environment, a robot is able to become more flexible, precise, and capable. As a leading robotic arm manufacturer, Flexiv combines precision with human-like intelligence and flexibility to meet evolving industry demands.
Finally, customization and scalability are becoming increasingly vital as manufacturers demand modular production lines that can ramp up, ramp down, or change over as demand fluctuates.
At Flexiv, we are committed to pushing the boundaries of manufacturing by creating adaptive robots that combine precision with human-like intelligence and flexibility.
For manufacturers looking to stay ahead, investing in these next-generation robotic solutions is essential for maximizing productivity, improving quality, and achieving a strong return on investment.





